TomGEM scientists isolate mutants exhibiting enhanced heat tolerance
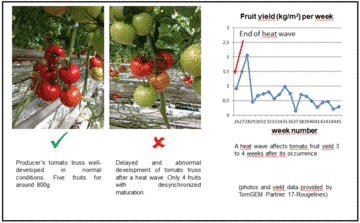
Heat waves during the last summers have affected the production of fruits in tomato plants. Tomato producers observed significant modifications associated with these high temperature circumstances, among which a severe reduction in fruit number as illustrated by the figure below.
In an attempt to address this important issue within the frame work of the H2020 TomGEM project, scientists have explored a large collection of 4000 tomato mutants allowing the isolation of several mutants exhibiting enhanced tolerance to high ambient temperatures. Subsequently, they were able to show that the loci conferring the tolerance can be transferred to other tomato cultivars by classical crossing.
The next steps will now focus on the identification of the genes underlying the observed heat tolerance character and the deciphering of the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in this trait.